What Are the Compostable Standards in the United States, and How Can They Be Obtained?
Are you confused about the compostable standards and certifications in the United States? Then this article is for you!
ASTM D6400 protocols and standards are used to test commercially compostable bags, containers, and other products in the United States. ASTM is the American Society for Testing and Materials.
The Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) provides certification for commercially compostable products. However, no equivalent home compost standards have been established in the United States at the moment.
Keep reading to take an in-depth look at the required ASTM D6400 tests, the process of obtaining a BPI certification, and the benefits of taking this action.
Achieving Compostable Certification in the USA: A Comprehensive Guide
In 2019, the United States accounted for the second-largest share of plastic use worldwide, at just over 18 percent. This is followed by the generation of around 73 million metric tons of plastic waste in the same year.
The United States is estimated to increase that number up to 90 million metric tons by 2030! Can you imagine the impact of such massive amounts of plastic waste on our environment and daily lives?
This is where compostable standards come in.
Adhering to compostable standards, organic recycling methods become a viable option to treat plastic waste, establishing more effective waste management and true circular resource preservation.
Then, comes the role of certification in deeming bags and sorts of containers as commercially compostable. This label means that the product in question can undergo efficient aerobic composting.
Let’s take a closer look at the standards of being a commercially compostable product, how to obtain compostable certification, and what the pros of this process are.
Standards According to the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM)

A commercially compostable product, also referred to as industrially compostable, is a product that transforms into useful under two particular conditions:
- An increased temperature
- A specifically developed microbial content
To classify a product as commercially compostable or industrially compostable, it needs to earn the label by getting certified after passing several tests and criteria.
In the United States, the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has specifications set to determine whether or not a plastic or plastic-made product can be considered commercially compostable.
To be more exact, these standard specifications are enforced by the ASTM D6400; a biodegradation test consisting of four parts.
According to the ASTM, a commercially compostable product is designed to successfully undergo aerobic composting; a type of composting that requires regularly introducing oxygen (by periodic tumbling), bacteria, and elevated temperatures.
An example of commercially compostable products is polylactic acid materials (PLAs).
Here are some of the ASTM D6400 protocols for commercially compostable products in the United States:
- A time frame of 180 days must be met. Within this period, both physical breakdown (disintegration) and chemical breakdown (biodegradation; the formation of compost) of the material must happen.
- Within the 180-day time frame, the material must reach at least 90 percent conversion of the carbon in its compositions into carbon dioxide. In other words, 90 percent or more of the material should be converted by microorganisms into carbon dioxide.
- The final product of the material’s composting must be non-toxic; has no negative impact on the surrounding ecosystem.
The conditions of the ASTM D6400 test seem to favor bacteria that thrive in temperatures above 122 degrees Fahrenheit (50 degrees Celsius). It’s also specific for composting in industrial facilities, not home compost facilities.
The Next Step at the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI)
The ASTM isn’t the end of the line for a product to be classified as commercially compostable. Once the product passes all the required tests, the results can be sent for certification to a third-party organization.
Not only is the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) in the United States one of those third-party organizations, but also a leading authority across all of North America regarding compostable products.

The BPI certification is the most widely recognized, reliable third-party assurance of whether or not a product meets compostability standards set by the ASTM. This certification program has been in practice for more than two decades.
To obtain BPI certification, a product must also meet eligibility requirements, fluorinated chemicals standards, and labeling requirements.
BPI-certified products are added to an online database to let audiences verify the certification of items they want to check independently.

Steps to Obtain Compostable Certification in the United States
To get a product certified as commercially compostable or industrially compostable, the following steps are necessary:
1. Submitting a complete application
First, you need to submit the correct, complete application form to the BPI. For new companies, a confidentiality agreement and a member profile must be submitted once.
For a new application, the documents needed are:
- BPI application
- BPI product worksheet
- BPI PFA form
- Photo of product
- A safety data sheet for each ingredient used in the material
A BPI project manager will contact you after submission to work out the rest of the certification process.
2. Paying the fees
Next, you need to pay the necessary fees for both certification and membership in BPI. Until the transaction is complete, the application won’t move forward.
You can check the exact fees required from the official BPI website.
3. Conducting required tests
After successful application submission and payment, a technical review assigned to the project by BPI will design a test scheme for the product to be certified.
The identified tests must be done by an external lab that’s approved by the BPI. Once the results are in, they’re then sent to the BPI so the application can progress to the technical review stage.
4. Starting the technical review
This phase begins when the applicant sends all the necessary test reports to the technical reviewer, including a verification report for the provided samples.
This step ensures that the product meets both ASTM standards and BPI protocols.
5. Finalizing license agreement
This phase comes after the technical review is successfully finished.
The license agreement document provides a detailed overview of the BPI certificate usage rights.
It also explains further aspects of the program including information on certificates, recertification requirements, termination, and control/inspection.
6. Completing certification
In this final stage, the project manager sends the member the following items for the certified product:
- Final review summary
- A copy of the license agreement
- Download links for the artwork files of the certification mark
- BPI certificate in PDF format
How long does the certification process take?
The entire certification process usually takes up to six months. It can require more time depending on the type of test scheme as well as how ready and attentive the applicant is.
Most of the time, the longest step of the certification process is testing.
Tests such as FTIR, ash, and metal can be done in under a month, while tests like disintegration take at least three months. Biodegradation tests require at least six months.
Once all the test results are in and the samples are received, the technical review step typically takes around a month.
Benefits of Obtaining Compostable Certification in the United States
Obtaining a compostable certification is surely a lot of work, but it offers crucial benefits.
First, a compostable certification is represented as a logo on the product (such as compostable dog poop bags).
This instantly boosts your marketability because consumers can immediately recognize that this product has passed strict testing to prove it’s compostable.
As a result, customers become more confident about buying the product because they can be comfortable throwing the waste in the trash while knowing they’re helping the environment.
In addition to promoting the credibility of your product and company, a compostable certification improves the sustainability of your production resources for future generations.
Not to mention, your company’s environmental impact will be more positive, so you’ll be doing your part in reducing pollution of our planet.
FAQs
Is compostable really compostable?
A container or bag certified/labeled as compostable by the ASTM and BPI is made to be composted in industrial composting facilities.
Such products are not suitable for home composting.
Currently, equivalent standards for home compost certification are yet to be established in the United States, unlike protocols in Europe like the ones specified by TUV Austria.
How do you know if something is compostable?
A product (bag or container) is compostable only if it shows the official label. In the United States, this label is the ASTM or BPI logo.
What is compostable vs biodegradable?
Compostable means that the material is engineered to biodegrade and become exclusively soil-enriching matter. On the other hand, a biodegradable material breaks down and incorporates into soil or water.
Is ASTM D6400 BPI certified?
Yes. Once a product passes ASTM D6400 testing, it can apply for BPI certification.
What is the Difference Between Compostable Standards and Certification?
Compost standards are the set of specifications that must be met by solid material biodegradation for the product to be labeled commercially compostable.
Compostable certification is proof that the bag or container has met the compostable standards.
What is the equivalent of ASTM D6400 in other countries?
In Europe, the equivalent is EN 13432 standard.
In Australia and New Zealand, the equivalent is the Australian Bioplastics Association (ABA) Standard 4736-2006.
See the infographic below to better understand the standards and certifications in the US and internationally.
Compostability and Biodegradability, Standards and Certifications Summary
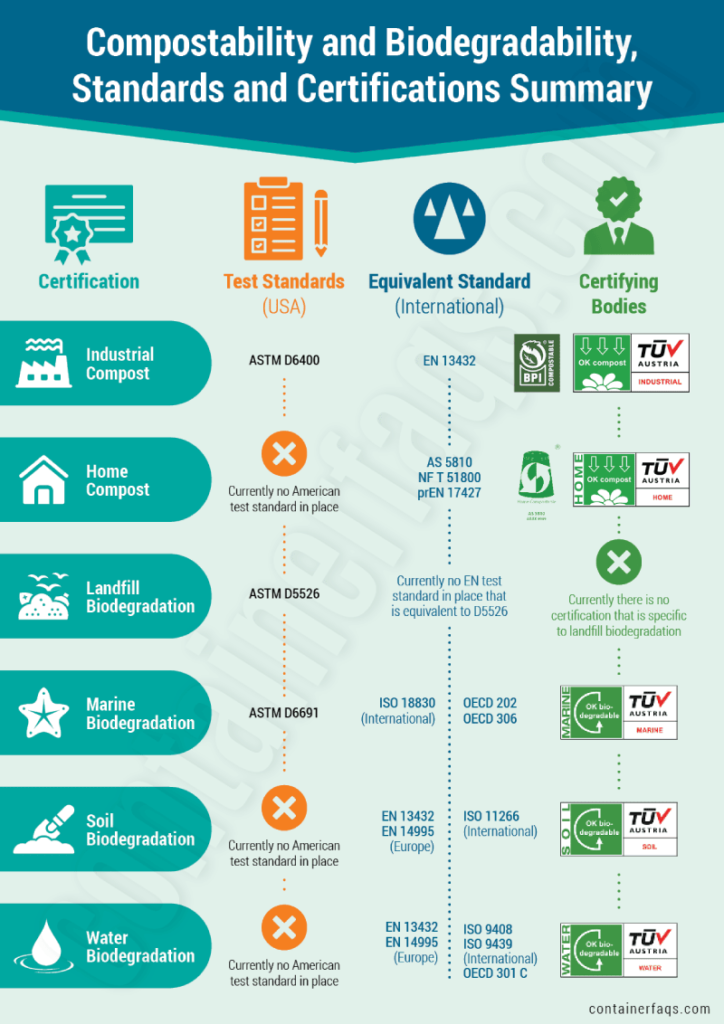
Conclusion
While the ASTM has set standards for commercially compostable products, a certification is required after passing the tests to prove all the conditions have been met.
With plastic waste polluting lands, air, oceans, food, and even human blood, compostable standards are more critical than ever in the United States.
As always, feel free to comment below if you have any questions or entries!
Sources






